Satellites are celestial bodies that revolve around planets
without any heat and light of their own.
Satellite definition Acc. to NASA
A satellite is a moon, planet, or machine that orbits a
planet or star. For example, Earth is a satellite because it orbits the sun.
Likewise, the moon is a satellite because it orbits Earth. Usually, the word
"satellite" refers to a machine that is launched into space and moves
around Earth or another body in space
Why do we need a Satellite?
World First Satellite
The Sputnik 1 spacecraft was the first artificial satellite
successfully placed in orbit around the Earth and was launched from Baikonur
Cosmodrome at Tyuratam (370 km southwest of the small town of Baikonur) in
Kazakhstan, then part of the former Soviet Union.
 |
| Sputnik |
How does Satellite Work?
 |
| Path of satellite |
Parts of Satellite
Pakistani Satellites
Paksat-1
Paksat-1, also known as Palapa-C1, HGS-3, and Anatolia-1, was a geosynchronous and communications satellite made and owned by the Boeing Company. It was leased to SUPARCO and changed its name to Paksat-1. On February 1st, 1996, it was successfully launched into orbit as Palapa-C1 with Indonesia serving as its initial customer. However, following the technical issues, the satellite was leased to SUPARCO in December 2002 and placed in an orbit with a 38° East longitude. Over 75 nations in Europe, Africa, the Middle East, South Asia, and Central Asia are covered by Paksat-1's C-band and Ku-band services. Government agencies, television networks, telecommunications firms, and data and broadband internet service providers were among its clients.
- Internet backbone extension
- Point-to-point data services
- Remote Internet access
- Broadcast services (video and data)
- Business VSAT networks
- Direct-to-home
Pakistan Technology Evaluation Satellite (PakTES-1A)
PakTES-1A is a satellite that SUPARCO scientists, engineers, and technicians created on their own. PakTES-1A's main goal is to make the next significant advancement in establishing the domestic capability for the design and development of various kinds of satellites.
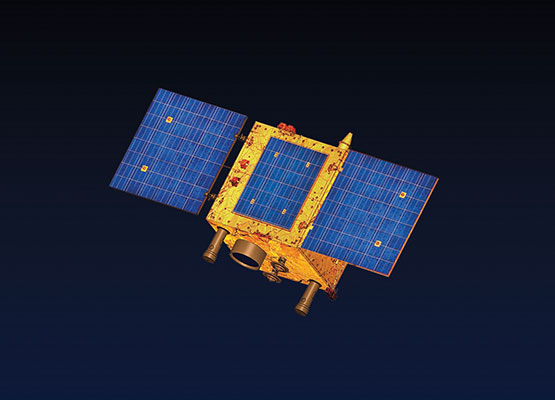
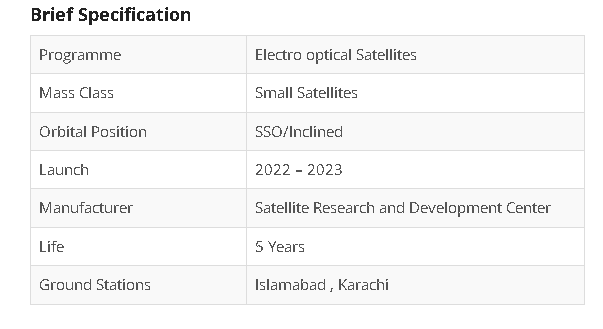
PAKISTAN REMOTE SENSING SATELLITE (PRSC-EOS)
To build and launch three additional optical remote sensing satellites by the year 2023, SUPARCO has launched the PRSC-EOS optical remote sensing application satellites initiative.
The satellites will join Pakistan's fleet of PRSS-1 and PakTES-1A remote sensing satellites that are currently in space. The domains of land mapping, agriculture categorization and assessment, urban and rural planning, environmental monitoring, natural disaster monitoring and management, surveying, protection of natural resources, and others will all make use of the remote sensing data.





Comments
Post a Comment